China’s economic downturn poses a significant long-term challenge for the country. The slowing growth rate, declining consumer confidence, and increasing debt levels are all contributing to this challenging economic climate. One of the key factors driving this downturn is the ongoing trade war with the United States, which has resulted in tariffs on billions of dollars worth of Chinese goods.
This has had a negative impact on Chinese exports and has led to a decrease in foreign investment in the country. Additionally, China’s aging population and rising labor costs have also put pressure on the economy, as the country grapples with how to sustain its rapid economic growth of the past few decades. In response to these challenges, the Chinese government has been implementing various stimulus measures to boost the economy, including tax cuts, increased infrastructure spending, and monetary easing.
However, these measures may only provide short-term relief and could potentially exacerbate existing issues such as debt levels and overcapacity in certain industries. Moving forward, China will need to address structural issues within its economy, such as increasing domestic consumption, reducing reliance on exports, and improving the efficiency of state-owned enterprises. This will require significant reforms and a long-term strategic vision to ensure sustainable and inclusive growth for the country in the years to come.

Understanding the Causes Behind China’s Persistent Economic Decline
China’s persistent economic decline can be attributed to a variety of factors that have been at play for many years. One major cause is the country’s aging population, which has resulted in a shrinking workforce and a decrease in productivity. Additionally, China’s reliance on manufacturing and exports has made it vulnerable to fluctuations in global demand and competition from other countries.
The government’s strict control over the economy and lack of transparency have also hindered economic growth, as investors are hesitant to invest in a market that lacks clear regulations and protections. Furthermore, widespread corruption and nepotism have eroded trust in the government and business sector, leading to a lack of confidence in the economy. The country’s environmental degradation and resource depletion have also had a negative impact on the economy, as the costs of pollution and resource scarcity continue to rise.
In order to address these issues and reverse the economic decline, China must focus on diversifying its economy, investing in education and technology, promoting innovation and entrepreneurship, and implementing policies that promote sustainability and accountability. By addressing these root causes, China can work towards a more stable and prosperous economic future.
The Impact of Domestic Policies on China’s Economic Performance
Domestic policies in China have had a significant impact on the country’s economic performance over the years. The Chinese government’s emphasis on promoting innovation and technology has helped fuel economic growth and modernization in various sectors. By investing heavily in research and development, China has been able to establish itself as a global leader in industries such as telecommunications, renewable energy, and e-commerce. Additionally, the government’s push for urbanization and infrastructure development has created new opportunities for economic growth, job creation, and enhanced productivity.
However, some critics argue that China’s strict regulations on foreign investment and intellectual property rights have hindered its economic performance by limiting competition and innovation. Despite these challenges, China’s economic growth has remained strong, driven by a combination of domestic policies aimed at stimulating growth, increasing consumer spending, and reducing income inequality. As China continues to navigate the complexities of its domestic policies, the world will be closely watching to see how these decisions will shape the country’s economic future.
Global Reactions to China’s Economic Struggles and Their Implications
China’s economic struggles have sparked a range of reactions from the international community, with implications that extend far beyond its borders. Many countries have expressed concern about the potential impact of China’s economic downturn on global markets and trade. Some have called for increased cooperation and support to help stabilize the Chinese economy, while others have taken a more cautious approach, fearing that China’s economic troubles could have negative consequences for their own economies.
In addition to economic concerns, there are also broader geopolitical implications to consider. As China’s economic power wanes, its influence on the global stage may diminish, leading to shifts in the balance of power and potential conflicts between major world powers. The reactions to China’s economic struggles vary widely depending on the country and its individual interests, but one thing is clear: these challenges have the potential to reshape the global economic and political landscape in ways that are still not fully understood.
It is crucial for countries to work together to find solutions that benefit all parties involved, rather than resorting to protectionism or isolationism in response to China’s economic woes. Only through cooperation and understanding can the international community navigate the uncertain waters ahead and ensure a stable and prosperous future for all.
Comparing China’s Current Economic Slump with Historical Trends
China’s current economic slump can be compared to historical trends to gain a better understanding of the factors at play. Throughout its history, China has experienced periods of economic growth and contraction, often in response to internal and external factors. The current slowdown can be attributed to a variety of issues, including the ongoing trade war with the United States, rising debt levels, and a shift towards a more consumer-driven economy. When comparing this slump to past economic downturns, it becomes clear that China has weathered similar challenges in the past and has the resilience to bounce back.
In the late 1990s, China faced a financial crisis that led to a significant slowdown in economic growth. However, through a combination of government stimulus measures and structural reforms, China was able to emerge from the crisis stronger than before. Similarly, during the global financial crisis of 2008, China implemented a massive stimulus package that helped to mitigate the impact of the downturn on its economy. By examining these historical trends, it is evident that China has the capacity to overcome its current economic challenges and return to a path of sustainable growth. The key will be for the government to implement effective policies that address the underlying issues contributing to the slump and support the economy in transitioning to a more sustainable growth model.
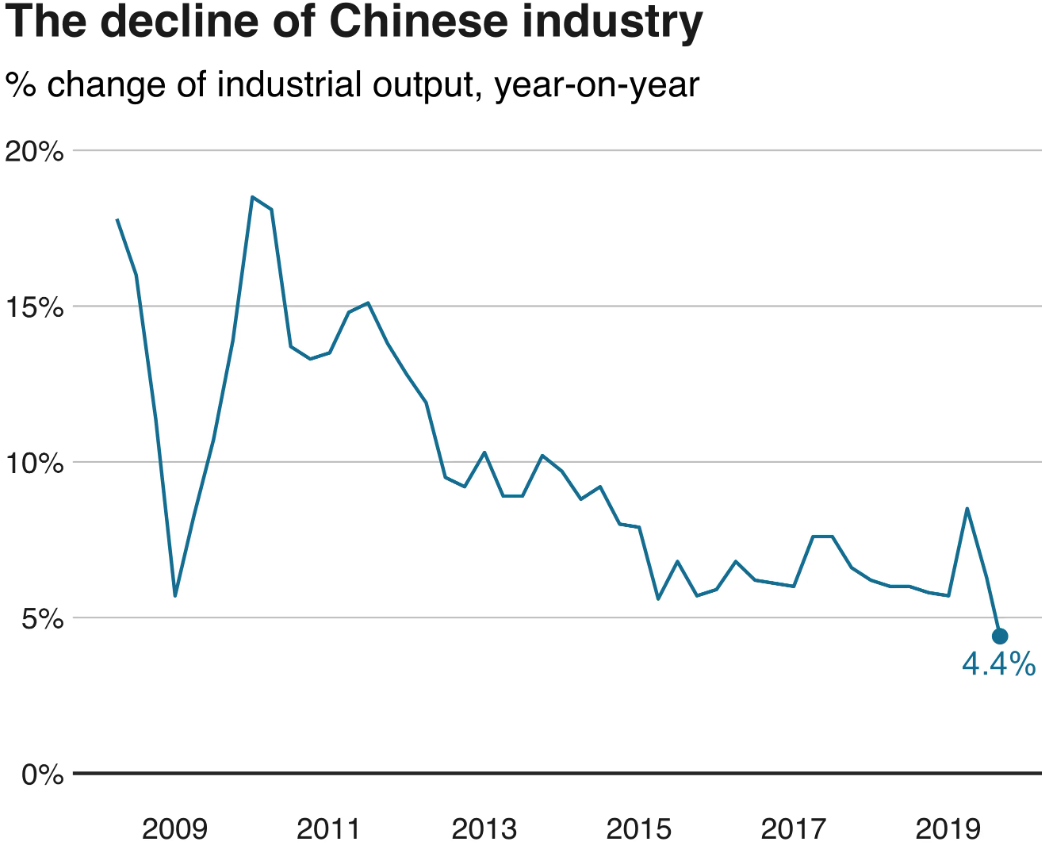
Potential Strategies for China to Overcome Its Economic Challenges
China faces a number of economic challenges that require strategic solutions to overcome. One potential strategy is to focus on increasing domestic consumption to reduce reliance on exports. By enhancing consumer purchasing power through wage growth and social welfare policies, China can stimulate demand for domestic goods and services, which in turn can boost economic growth. Another strategy is to promote innovation and technological advancement to drive productivity and competitiveness in key industries.
By investing in research and development and fostering a culture of entrepreneurship, China can position itself as a global leader in high-value-added industries, such as artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and renewable energy. Additionally, China can improve its regulatory environment and strengthen intellectual property rights protection to attract more foreign direct investment and encourage innovation. Furthermore, China can address income inequality and regional disparities by implementing targeted policies to support rural development and improve access to education and healthcare in underdeveloped regions.
By promoting inclusive growth, China can ensure that the benefits of economic development are shared more equitably across society. Overall, by implementing a combination of these strategies, China can navigate its economic challenges and achieve sustainable long-term growth.
